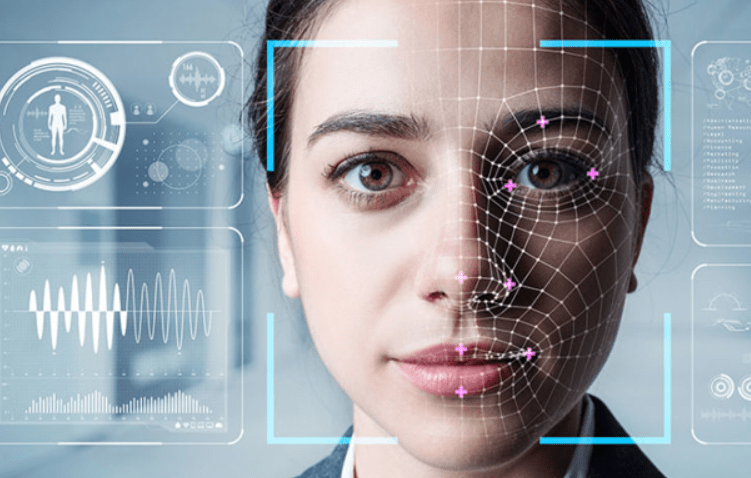
In an age of digital convenience, our faces have become keys. From unlocking our phones or laptops to accessing bank accounts and high-security facilities, our fingerprints, voices, and faces have become the keys to our identities. But with increased reliance on facial recognition comes a growing threat that is presentation attacks or “spoofing”. That’s where face liveness detection becomes critical to securing biometric systems. Face liveness detection is a sophisticated security layer within facial recognition systems. It’s designed to determine if the face being presented to a camera is from a living, physically present person – as opposed to a photograph, video, mask, or synthetically generated image.
Face Liveness Detection
Why Face Liveness Detection Matters?
As facial recognition becomes more common, so do sophisticated attempts to fool these systems. Face liveness detection is the countermeasure, adapting to block evolving threats like deepfakes and ensuring our faces remain secure forms of identification.
[table id=47 /]
How Does Face Liveness Detection Work?
There are several approaches to facial liveness detection. Listed below are some of the major methods of Face Liveness Detection:
Passive Liveness Detection
Not active-passive methods analyze a single image or a brief video of the face without requiring any specific action from the user. Passive methods look for:
- Micro-movements: Our eyes blink naturally, and our facial muscles twitch subtly. Passive systems can detect these minute movements.
- Skin Texture: Human skin has specific texture characteristics not readily replicated in photos or masks.
- 3D Analysis: Some solutions analyze if the presented face is three-dimensional versus a flat image.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Passive Face Liveness Detection
[table id=48 /]
Active Liveness Detection
Active systems prompt the user to perform specific actions to prove they are alive:
- Following Instructions: The system might request a head turn, smile, a blink, or even a spoken phrase.
- Challenge-Response: The user responds to a visual prompt, like repeating a gesture or moving their head in a particular pattern.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Active Face Liveness Detection
[table id=49/]
Hardware-Based Liveness Detection
These systems use specialized cameras or sensors to capture more data than a standard camera:
- Infrared and 3D sensors: These can detect depth and heat, helping differentiate between a living face and an image.
- Texture Analysis: Some solutions perform highly detailed texture analysis to pick up on irregularities in artificial reproductions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hardware-Based Detection
[table id=50 /]
Technical Elements to implement Face Liveness Detection in Biometric Security
Integrating face liveness detection into a biometric security system requires careful consideration of various technical elements. These elements range from hardware and software needs to the algorithms and security protocols that will ensure the system’s effectiveness and reliability. Let’s break down some of the key technical requirements:
[table id=51 /]
Measuring Face Liveness Detection Effectiveness
Several metrics are used by researchers and vendors to benchmark the accuracy and robustness of face liveness detection systems:
- Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (APCER): Percentage of fake/spoofing presentations incorrectly classified as live by the system.
- Bona fide Presentation Classification Error Rate (BPCER): Percentage of real live presentations incorrectly classified as fake by the system.
- Average Classification Error Rate (ACER): Average of APCER and BPCER. Lower is better, with a goal below 1% for high-security applications.
- Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis: Plots TPR vs FPR values at different classification thresholds to illustrate trade-offs between security/usability. Area Under the Curve (AUC) measures overall discriminability capacity.
- Equal Error Rate (EER): Point where FPR and FNR are equal, conventionally accepted as a single representative metric. A good system has EER below 1%.
Conclusion
Face liveness detection plays a fundamental role in developing the trustworthiness and robustness of biometric systems that authenticate users via facial recognition. As spoofing attacks become ever more sophisticated, continuous innovation is crucial to maintain an edge over evolving security threats through ongoing methodological and technical advances. With prudent safeguards around appropriate uses, consent, privacy, and accountability, biometrics including facial liveness verification hold much promise to deliver convenient identity proofing at scale.